PKA - SPR Binding Assay
Our service for comprehensive kinetic characterization of your small molecule kinase inhibitors
Theoretical background: cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) is a tightly regulated enzyme, functioning as an on/off switch in intracellular signal transduction. The inactive holoenzyme, consisting of two dimeric regulatory (R-) subunits and two catalytic subunits, is activated upon binding of the second messenger cAMP to the two highly conserved cyclic-nucleotide-binding domains of the R subunits.
PKA and inhibitors: The isoquinoline derivative H89 and KT 5720, one of a family of compounds synthesized from the fungus Nocardiopsis sp., act as specific competitive antagonists of the PKA catalytic subunit with respect to ATP. However, a number of recent studies have identified effects of H89 (Ki = 48 nM [1]) and KT 5720 that are independent on PKA inhibiton including actions on other protein kinases and signaling molecules and on basic cellular functions, such as transcription.
The heat stable protein kinase inhibitor PKI is a thermostable pseudo substrate inhibitor, which mimics the kinase substrate by binding to the catalytic site of the catalytic subunits of PKA via the arginine-cluster basic subsite.
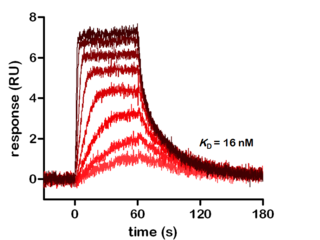
Figure: Real-time kinetic analysis of kinase inhibitor H-89 binding to PKA Cα using surface plasmon resonance.
[1] Chijiwa T et al. (1990) J Biol Chem. 25;265(9):5267-72.
Please contact our application specialists to obtain more information and an individual quote tailored to your specific needs.
Tel.: +49 (0) 561-804 4661 | Fax: +49 (0) 561-804 4665 | info@biaffin.de
We value your privacy
In order to optimize our website for you and to be able to continuously improve it, we use cookies. Further information is available in our Data Protection Statement. Here you can find our Legal Information.